Scientists reveal different water isotope concentrations in precipitation observations across Brazil’s diverse climate
An isotope of a chemical element contains the same number of protons in the center of its atom, but when compared to another atom, the number of neutrons is different. Regarding water, some hydrogen and oxygen atoms within water molecules contain different number of neutrons, resulting in water isotopes. Because of the wide range of interactions that water molecules within precipitation can have with the surrounding atmosphere, research collaborators from Brazil and the United States have come together to gain a better understanding of the different isotopes of water that naturally occur within precipitation.
The research team developed an experiment in which they set up four rain collection stations across central-southeastern Brazil. In each sample, they sought out different isotopes of water molecules at both daily and monthly intervals. On top of isotopic composition of water, they also explored how regional circulation patterns, atmospheric systems, and moisture sources and transport affect precipitation isotopes differently at each location.
To provide high quality moisture transport data, the team used the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model for air mass trajectories. Surface and atmospheric composition data came from reanalysis, and the ECMWF ERA-interim system generated convective/stratiform precipitation data. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences just published their full study.
“The amount effect, or high precipitation, is correlated with lower values of isotopic composition, in tropical areas,” said the study’s corresponding author Dr. Didier Gastmans, Researcher at the São Paulo State University, Environmental Studies Center.
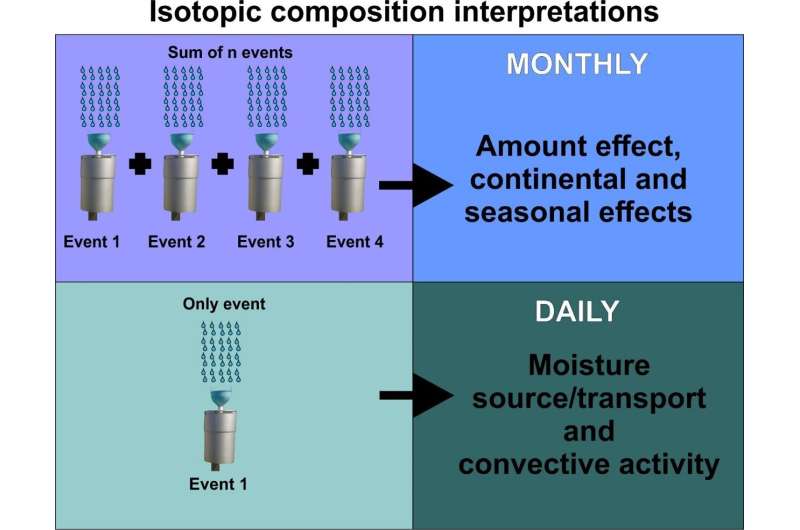
According to Dr. Gastmans, it is critical to study rainwater’s isotopic composition throughout a given month. With monthly data, scientists can determine the different composition effects in continental regions versus coastal regions. They found a larger sample of different isotopes of water in continental areas comparted to the coast. Regarding seasonal variation, isotopic composition varies between wet and dry season. During the dry season, when rain occurs, isotopic composition is high, but during the wet season, rainwater is mostly composed of similar isotopes.
However, when considering daily measurements, interpreting the isotopic composition is more complex. Moisture source and transport, convective activity, and local factors all play a bigger role in determining rainfall type compared to monthly measurements, especially in Tropical regions.
This is due to monthly measurements representing a sum of individual rainfall events. Daily readings tell a better story of the influences that a particular storm or atmospheric profile has on the region.
“Now we are analyzing the isotopic composition of precipitation by intra-events, that is, every 5 minutes,” said Prof. Gastmans.
Continuously decreasing the interval between measurements will allow future research to have more insight into rainfall type classification as well as isotopic interactions and processes beneath the cloud, according to Dr. Gastmans.
Influence of laboratory preparations in climatic studies that use isotopes
Vinícius dos Santos et al, Distinguishing the Regional Atmospheric Controls on Precipitation Isotopic Variability in the Central-Southeast Portion of Brazil, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s00376-022-1367-0
Citation:
Scientists reveal different water isotope concentrations in precipitation observations across Brazil’s diverse climate (2022, May 18)
retrieved 18 May 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-05-scientists-reveal-isotope-precipitation-brazil.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
An isotope of a chemical element contains the same number of protons in the center of its atom, but when compared to another atom, the number of neutrons is different. Regarding water, some hydrogen and oxygen atoms within water molecules contain different number of neutrons, resulting in water isotopes. Because of the wide range of interactions that water molecules within precipitation can have with the surrounding atmosphere, research collaborators from Brazil and the United States have come together to gain a better understanding of the different isotopes of water that naturally occur within precipitation.
The research team developed an experiment in which they set up four rain collection stations across central-southeastern Brazil. In each sample, they sought out different isotopes of water molecules at both daily and monthly intervals. On top of isotopic composition of water, they also explored how regional circulation patterns, atmospheric systems, and moisture sources and transport affect precipitation isotopes differently at each location.
To provide high quality moisture transport data, the team used the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model for air mass trajectories. Surface and atmospheric composition data came from reanalysis, and the ECMWF ERA-interim system generated convective/stratiform precipitation data. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences just published their full study.
“The amount effect, or high precipitation, is correlated with lower values of isotopic composition, in tropical areas,” said the study’s corresponding author Dr. Didier Gastmans, Researcher at the São Paulo State University, Environmental Studies Center.
According to Dr. Gastmans, it is critical to study rainwater’s isotopic composition throughout a given month. With monthly data, scientists can determine the different composition effects in continental regions versus coastal regions. They found a larger sample of different isotopes of water in continental areas comparted to the coast. Regarding seasonal variation, isotopic composition varies between wet and dry season. During the dry season, when rain occurs, isotopic composition is high, but during the wet season, rainwater is mostly composed of similar isotopes.
However, when considering daily measurements, interpreting the isotopic composition is more complex. Moisture source and transport, convective activity, and local factors all play a bigger role in determining rainfall type compared to monthly measurements, especially in Tropical regions.
This is due to monthly measurements representing a sum of individual rainfall events. Daily readings tell a better story of the influences that a particular storm or atmospheric profile has on the region.
“Now we are analyzing the isotopic composition of precipitation by intra-events, that is, every 5 minutes,” said Prof. Gastmans.
Continuously decreasing the interval between measurements will allow future research to have more insight into rainfall type classification as well as isotopic interactions and processes beneath the cloud, according to Dr. Gastmans.
Influence of laboratory preparations in climatic studies that use isotopes
Vinícius dos Santos et al, Distinguishing the Regional Atmospheric Controls on Precipitation Isotopic Variability in the Central-Southeast Portion of Brazil, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s00376-022-1367-0
Citation:
Scientists reveal different water isotope concentrations in precipitation observations across Brazil’s diverse climate (2022, May 18)
retrieved 18 May 2022
from https://phys.org/news/2022-05-scientists-reveal-isotope-precipitation-brazil.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
