Scientists uncover a causal relationship between remote extreme heat and the Canadian wildfires in 2023
Wildfires are events that can have significant impacts on ecosystems and human society. In the context of global warming, there has been a notable surge in the frequency and ferocity of wildfires in the Northern Hemisphere over recent years. In 2023, Canada experienced an unprecedented wildfire event, with CO2 emissions increasing by 527.1% over the average of 2001–2022 during the months of May–August.
The burned area was more than 6–7 times larger than in a normal year. Notably, both Canada and more than 15 states in the northeastern United States grappled with severe disruption to air quality as a result of this cataclysmic event.
The research group of Prof. Xu Yue from Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, China, investigated the meteorological factors that ignited this catastrophic event while also deliberating on the prospective triggers and ramifications of wildfires in North America. The results have recently been published in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters.
According to this research, a noteworthy correlation between the occurrence of severe wildfires and anomalies in maximum temperatures was revealed.
“During periods of high wildfire emissions, maximum temperatures were significantly higher than in periods with low emissions. Conversely, the average precipitation during periods of high wildfire emissions did not exhibit a statistically significant departure from that during periods of low wildfire emissions. Additionally, the phenomenon of ‘rain and wildfires at the same time’ was observed,” explains Prof. Yue.
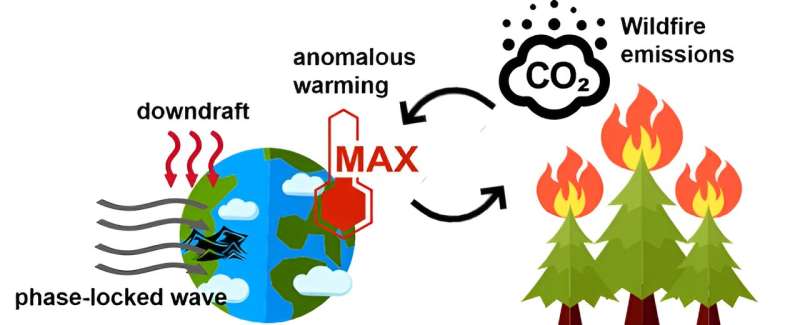
Further investigations identified notable high-temperature anomalies within the primary burn area during the 2023 Canadian wildfire eruption period. This occurrence coincided with the enduring presence of anomalous high-pressure systems over the region attributable to Rossby wave dispersion. The persistent downdraft resulted in a sustained elevation of near-surface temperatures, thereby fostering conditions conducive to wildfire.
A similar “phase-locked” phenomenon of persistent geopotential height anomalies also emerged as the principal catalyst behind the unprecedented heat wave event in North America in 2021.
“Owing to the distinctive topographical features of the Rocky Mountains, phase-locked related heat is more prone to occur in west-central Canada, consequently heightening the risk of intensified wildfire events,” adds Prof. Yue.
Recurrent and severe wildfires in this area could exacerbate the warming trend through the CO2 emissions generated. Concurrently, the amplification of global warming may increase the availability of fuel in the future. Hence, greater efforts will be needed to maintain public health and ecosystem functions within affected regions.
More information:
Yihan Hu et al, Climatic drivers of the Canadian wildfire episode in 2023, Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.aosl.2024.100483
Citation:
Scientists uncover a causal relationship between remote extreme heat and the Canadian wildfires in 2023 (2024, March 20)
retrieved 20 March 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-03-scientists-uncover-causal-relationship-remote.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Wildfires are events that can have significant impacts on ecosystems and human society. In the context of global warming, there has been a notable surge in the frequency and ferocity of wildfires in the Northern Hemisphere over recent years. In 2023, Canada experienced an unprecedented wildfire event, with CO2 emissions increasing by 527.1% over the average of 2001–2022 during the months of May–August.
The burned area was more than 6–7 times larger than in a normal year. Notably, both Canada and more than 15 states in the northeastern United States grappled with severe disruption to air quality as a result of this cataclysmic event.
The research group of Prof. Xu Yue from Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, China, investigated the meteorological factors that ignited this catastrophic event while also deliberating on the prospective triggers and ramifications of wildfires in North America. The results have recently been published in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters.
According to this research, a noteworthy correlation between the occurrence of severe wildfires and anomalies in maximum temperatures was revealed.
“During periods of high wildfire emissions, maximum temperatures were significantly higher than in periods with low emissions. Conversely, the average precipitation during periods of high wildfire emissions did not exhibit a statistically significant departure from that during periods of low wildfire emissions. Additionally, the phenomenon of ‘rain and wildfires at the same time’ was observed,” explains Prof. Yue.
Further investigations identified notable high-temperature anomalies within the primary burn area during the 2023 Canadian wildfire eruption period. This occurrence coincided with the enduring presence of anomalous high-pressure systems over the region attributable to Rossby wave dispersion. The persistent downdraft resulted in a sustained elevation of near-surface temperatures, thereby fostering conditions conducive to wildfire.
A similar “phase-locked” phenomenon of persistent geopotential height anomalies also emerged as the principal catalyst behind the unprecedented heat wave event in North America in 2021.
“Owing to the distinctive topographical features of the Rocky Mountains, phase-locked related heat is more prone to occur in west-central Canada, consequently heightening the risk of intensified wildfire events,” adds Prof. Yue.
Recurrent and severe wildfires in this area could exacerbate the warming trend through the CO2 emissions generated. Concurrently, the amplification of global warming may increase the availability of fuel in the future. Hence, greater efforts will be needed to maintain public health and ecosystem functions within affected regions.
More information:
Yihan Hu et al, Climatic drivers of the Canadian wildfire episode in 2023, Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.aosl.2024.100483
Citation:
Scientists uncover a causal relationship between remote extreme heat and the Canadian wildfires in 2023 (2024, March 20)
retrieved 20 March 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-03-scientists-uncover-causal-relationship-remote.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
