The jump in global temperatures in September 2023 is difficult to explain by natural climate variability alone
September 2023 broke the global mean temperature record by a staggering 0.5° C difference from the previous record. A new study calls for further analysis of the impact of volcanoes and anthropogenic climate forcing on the new record.
September 2023 was the warmest September on record globally by a very wide margin. A new study by the scientists from the Finnish Meteorological Institute shows that it is highly unlikely that climate change and natural climate variability, such as the ongoing El Niño phenomenon, would be sufficient to cause the new record.
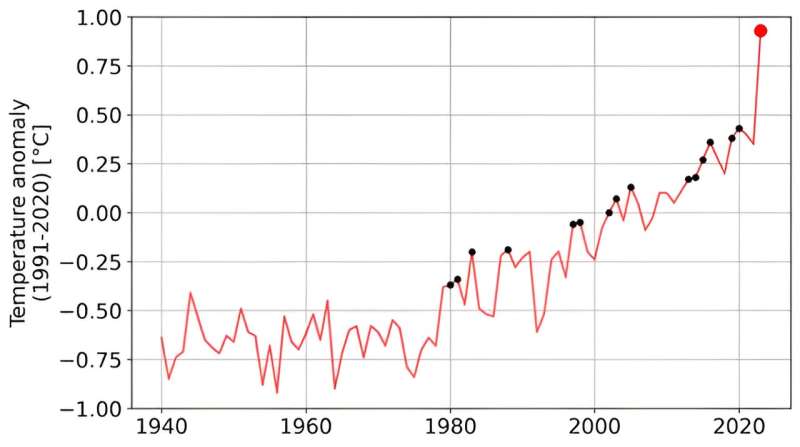
The global mean temperature in September 2023 was 0.93° C warmer than the 1991–2020 average, breaking the previous record set in 2020 by a margin of 0.5° C. This was the largest margin by which the previous monthly record has been broken in any calendar month.
The record margin for September 2023 was exceptional due to its timing. Typically, the biggest jumps in monthly temperatures are observed in the winter months, when the El Niño phenomenon, which raises global temperatures, reaches its peak. Consequently, the previous record high margin was observed in February 2016, supported by a strong El Niño. Unlike February 2016, the current El Niño was not near its maximum in September 2023.
What caused the high global temperature in September?
The unprecedented jump in average temperatures has puzzled scientists. Some scientists have argued that the half-degree margin between September 2020 and 2023 can be explained by ongoing climate change and natural climate variability, such as the change of a three-year La Niña into an El Niño.
Others have suggested that the Hunga-Tonga volcanic eruption in January 2021 or the reduction in sulfur emissions from shipping in 2020 may have contributed to the record temperatures of recent months.
A study published in npj Climate and Atmospheric Science has compared climate model-simulated record margins with observations.
It found that the observed record margin of 0.5° C is a very rare event in model simulations spanning from 1970 to 2050. Similar records occur in only about once in a hundred simulations.
The study estimated that the contribution of volcanic eruptions and reductions in sulfur emissions to the record margin could be around 0.1° C, which would significantly increase the likelihood of the September record.
More information:
Mika Rantanen et al, The jump in global temperatures in September 2023 is extremely unlikely due to internal climate variability alone, npj Climate and Atmospheric Science (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41612-024-00582-9
Provided by
Finnish Meteorological Institute
Citation:
The jump in global temperatures in September 2023 is difficult to explain by natural climate variability alone (2024, February 2)
retrieved 2 February 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-02-global-temperatures-september-difficult-natural.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
September 2023 broke the global mean temperature record by a staggering 0.5° C difference from the previous record. A new study calls for further analysis of the impact of volcanoes and anthropogenic climate forcing on the new record.
September 2023 was the warmest September on record globally by a very wide margin. A new study by the scientists from the Finnish Meteorological Institute shows that it is highly unlikely that climate change and natural climate variability, such as the ongoing El Niño phenomenon, would be sufficient to cause the new record.
The global mean temperature in September 2023 was 0.93° C warmer than the 1991–2020 average, breaking the previous record set in 2020 by a margin of 0.5° C. This was the largest margin by which the previous monthly record has been broken in any calendar month.
The record margin for September 2023 was exceptional due to its timing. Typically, the biggest jumps in monthly temperatures are observed in the winter months, when the El Niño phenomenon, which raises global temperatures, reaches its peak. Consequently, the previous record high margin was observed in February 2016, supported by a strong El Niño. Unlike February 2016, the current El Niño was not near its maximum in September 2023.
What caused the high global temperature in September?
The unprecedented jump in average temperatures has puzzled scientists. Some scientists have argued that the half-degree margin between September 2020 and 2023 can be explained by ongoing climate change and natural climate variability, such as the change of a three-year La Niña into an El Niño.
Others have suggested that the Hunga-Tonga volcanic eruption in January 2021 or the reduction in sulfur emissions from shipping in 2020 may have contributed to the record temperatures of recent months.
A study published in npj Climate and Atmospheric Science has compared climate model-simulated record margins with observations.
It found that the observed record margin of 0.5° C is a very rare event in model simulations spanning from 1970 to 2050. Similar records occur in only about once in a hundred simulations.
The study estimated that the contribution of volcanic eruptions and reductions in sulfur emissions to the record margin could be around 0.1° C, which would significantly increase the likelihood of the September record.
More information:
Mika Rantanen et al, The jump in global temperatures in September 2023 is extremely unlikely due to internal climate variability alone, npj Climate and Atmospheric Science (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41612-024-00582-9
Provided by
Finnish Meteorological Institute
Citation:
The jump in global temperatures in September 2023 is difficult to explain by natural climate variability alone (2024, February 2)
retrieved 2 February 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-02-global-temperatures-september-difficult-natural.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
