Boys choir found to compete sexually for female audiences through more energetic singing
Research led by Western Sydney University, Australia, has found that boys singing in a choir engage in simultaneous group cohesion and sexually motivated competition exhibited through voice modulation in the presence of a female audience.
In a paper, “Sex-related communicative functions of voice spectral energy in human chorusing,” published in The journal Biology Letters, the team explores the evolutionary origins of music, suggesting that it may have developed from capacities supporting both cooperation and competition.
Similar to interactive displays in non-human animals, human music may function both cooperatively and competitively, allowing different forms of communication to occur simultaneously at both group and individual levels.
The St Thomas Choir of Leipzig was studied to understand how male singers modify their behavior in the presence of female audience members. A previous study with the boy choir found that basses (the oldest boys with the deepest voices) exhibited increased energy in the “singer’s formant” frequency region when girls were in the audience.
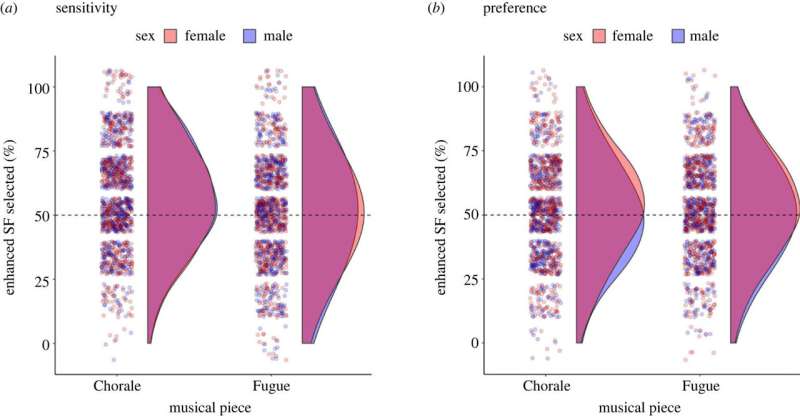
The study, conducted online, involved listening tasks to test female and male sensitivity and preferences for this subtle vocal modulation in choir performances. The study involved 679 females and 481 males in the sensitivity study and 655 females and 432 males in the preference study, with varying ages and musical training.
The stimulus set included audio excerpts from performances of a Chorale and a Fugue by the St Thomas Choir of Leipzig, with and without girls in the audience. Both female and male listeners were sensitive to increased high-frequency spectral energy in the singer’s formant, the especially energetic peaks that usually coincided with vowels.
Only female listeners exhibited a reliable preference for the enhanced singer’s formant, regardless of the type of musical piece. Male listeners did not show a preference for higher-energy singing, and those performing in the choir only enhanced that high energy when the audience included females.
The findings suggest that human chorusing represents a flexible form of social communicative behavior that brings out a subtle form of sexually motivated competition.
More information:
Peter E. Keller et al, Sex-related communicative functions of voice spectral energy in human chorusing, Biology Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2023.0326
© 2023 Science X Network
Citation:
Boys choir found to compete sexually for female audiences through more energetic singing (2023, November 10)
retrieved 13 November 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-11-boys-choir-sexually-female-audiences.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Research led by Western Sydney University, Australia, has found that boys singing in a choir engage in simultaneous group cohesion and sexually motivated competition exhibited through voice modulation in the presence of a female audience.
In a paper, “Sex-related communicative functions of voice spectral energy in human chorusing,” published in The journal Biology Letters, the team explores the evolutionary origins of music, suggesting that it may have developed from capacities supporting both cooperation and competition.
Similar to interactive displays in non-human animals, human music may function both cooperatively and competitively, allowing different forms of communication to occur simultaneously at both group and individual levels.
The St Thomas Choir of Leipzig was studied to understand how male singers modify their behavior in the presence of female audience members. A previous study with the boy choir found that basses (the oldest boys with the deepest voices) exhibited increased energy in the “singer’s formant” frequency region when girls were in the audience.
The study, conducted online, involved listening tasks to test female and male sensitivity and preferences for this subtle vocal modulation in choir performances. The study involved 679 females and 481 males in the sensitivity study and 655 females and 432 males in the preference study, with varying ages and musical training.
The stimulus set included audio excerpts from performances of a Chorale and a Fugue by the St Thomas Choir of Leipzig, with and without girls in the audience. Both female and male listeners were sensitive to increased high-frequency spectral energy in the singer’s formant, the especially energetic peaks that usually coincided with vowels.
Only female listeners exhibited a reliable preference for the enhanced singer’s formant, regardless of the type of musical piece. Male listeners did not show a preference for higher-energy singing, and those performing in the choir only enhanced that high energy when the audience included females.
The findings suggest that human chorusing represents a flexible form of social communicative behavior that brings out a subtle form of sexually motivated competition.
More information:
Peter E. Keller et al, Sex-related communicative functions of voice spectral energy in human chorusing, Biology Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2023.0326
© 2023 Science X Network
Citation:
Boys choir found to compete sexually for female audiences through more energetic singing (2023, November 10)
retrieved 13 November 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-11-boys-choir-sexually-female-audiences.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
